Linked list is a sequential/dynamic data structure. It is often used for constructing hash tables, trees, graphs, etc. What are the main differences of linked list with array and what are the pros/cons of linked list?
Advantages of Linked List
- Dynamic size: When we append a new element, unlike array, we do not have to create a room and shift all the elements. We simply make the pointer of the last element to point to the newly created node.
- Ease of insertion/deletion: Insertion and deletion operations are easy in linked list especially with the iterator. All we have to do is to manipulate the pointers. However, without the iterator, insertion/deletion would take O(n) same as array.
Disadvantages of Linked List
- No Random Access: In array, you can access an element with its index in a constant time. However, you cannot do the same in linked list. You must traverse from the head node until you find the desired node.
- Extra memory space for pointers: For each node, you need to assign a portion of memory for its pointer.
- Not cache-friendly: Unlike array, linked list data structure bundles memory spaces that are spread around the memory using pointer.
Operations/Time Complexity
- Access O(n)
- Unliked array, you cannot access with index. You must traverse from the head node until you reach the desired node. - Search O(n)
- Same as access - Insertion O(1) / O(n)
- With the iterator, “insertion” operation itself can be done in a constant time. Without the information of its location, you need to traverse starting from the head which takes O(n) - Deletion O(1) / O(n)
- Same as Insertion
Implementation with C++
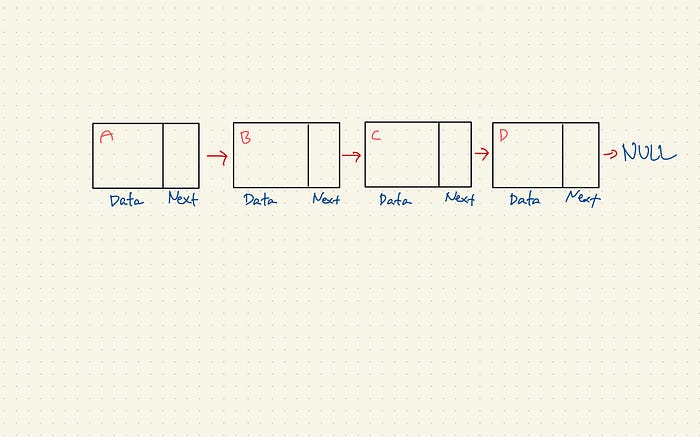
In this implementation of singly linked list, we will store three values for each node: key, value, next pointer. One of the reasons we store key is that every node in the linked list would have a different key so when we delete a specific node, we could distinguish by keys even if two nodes have same values.
Operations
Node* nodeExist(int k): returns NULL if it doesn’t exist, returns the address if it does.void appendNode(Node* node): Insert at the endvoid prependNode(Node* node): Insert at the beginningvoid insertNodeAfterKey(int k, Node* node): Insert after a specific keyvoid deleteByKey(int k): Delete node by its key
Code
[Contact]
✅ Email: changjin9792@gmail.com
✅ Github: https://github.com/JasonLee-cp
️✅ Medium: https://changjin9792.medium.com/

![[Leetcode] #1008 Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal(C++/Tree/Medium)](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/1*I4RG2CAiBIgoq31AVqJV2Q.jpeg)
![[Algorithm] Leetcode #91 Decode Ways (DP/Medium/C++) — How to solve ANY DP](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/1*Dl0F36mQqB_LNtA_dKd3ug.jpeg)
![[Algorithm] Longest Common Substring (C++/DP/Medium)](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/1*yuVzMhCJyDENbyhwAsrkwA.png)